In the realm of statistical analysis, there are generally two types of analysis that can be conducted: descriptive Statistics and Inferential Statistics. This article will discuss about the latter. Descriptive Statistics can be applied to members of a group or sample to summarize their characteristics concisely, providing us with information on the most important characteristics of the data collected. It’s typically the first type of analysis performed on any data set. The main characteristic unique to Descriptive Statistics that makes it distinct compared to Inferential Statistics is that we don’t draw any conclusions from this analysis. It is important to avoid making any pre-conceived conclusions about the data. Instead, we perform the analysis to gain a better understanding of the fundamental characteristics of the information. Most often, graphs, charts, and other techniques for visualization are employed in conjunction with summary tables that summarize the information for a simpler understanding.
There are four major kinds of Descriptive Statistics-
- Measures of Frequency
- Measures of Central Tendency
- Measures of Variability (Variation/Dispersion/Spread)
- Measures of Shape
Below are blog posts that explain each of these Descriptive Statistics.

MEASURES OF FREQUENCY
Measures of Frequency offer the most basic type of data, which is the way to determine the frequency that something occurs. This type of information assists us in creating very basic graphs and tables by using very basic arithmetic computations, like count, percentage, etc. We learn about the frequency of the values within the data, which provides us with frequency distributions. This distribution is plotted onto graphs, leading us to the Measures of Central Tendency notion.
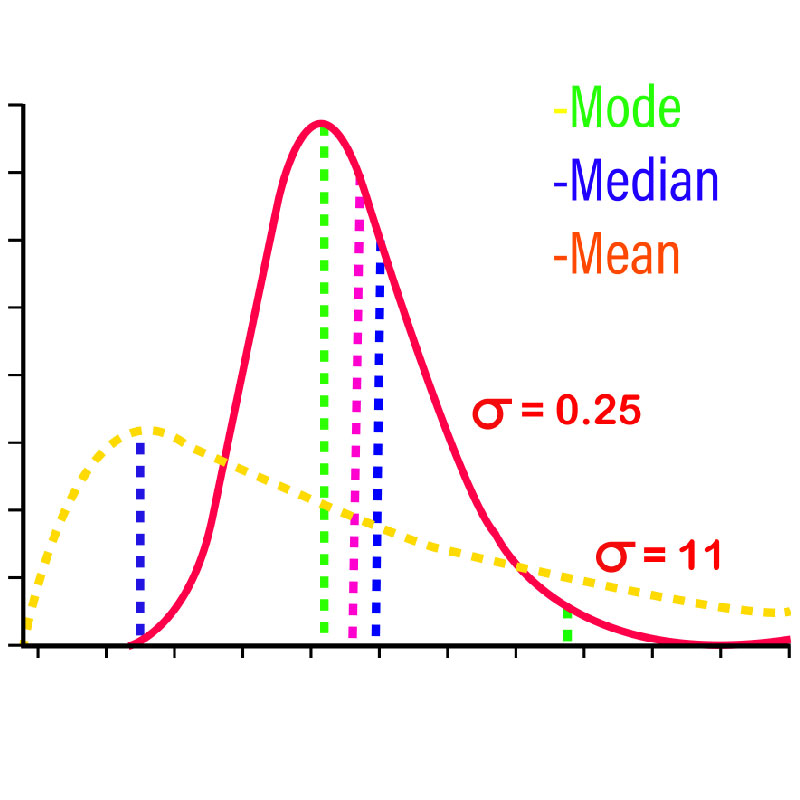
MEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY
The Measure of Central Tendency is a part of descriptive statistics, which allow us to define our data in one value. It is typically the one that is used to determine the central position in your data collection. The value can be determined through Mean, Median, and Mode, the three different Measures of Central Tendency. Each has its significance and can be utilized in various situations. It is crucial to keep in mind it is important to remember that Measures of Central Tendency are also named Measures of Central Location.
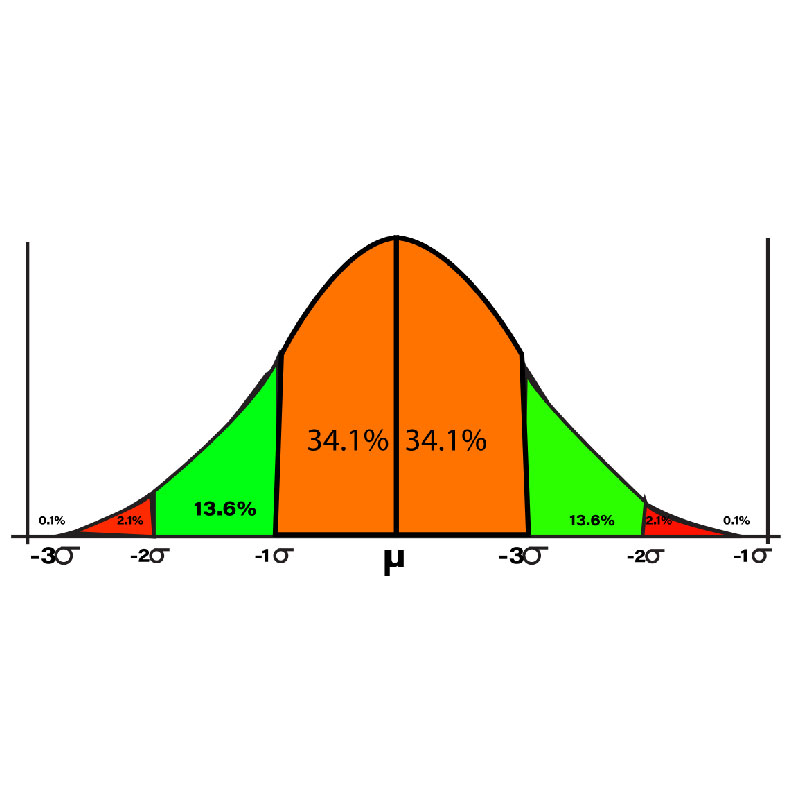
MEASURES OF VARIABILITY
These descriptive statistics aid in explaining the distribution of data. Different measures of variability can be used to explain how the data is dispersed. The data distribution will help understand how Inferential Statistics can be used to draw different conclusions about the population. The measures of variability include Variance, Range Standard Deviation, and Variance. And they play a significant part in nearly every type of analysis of statistical science.
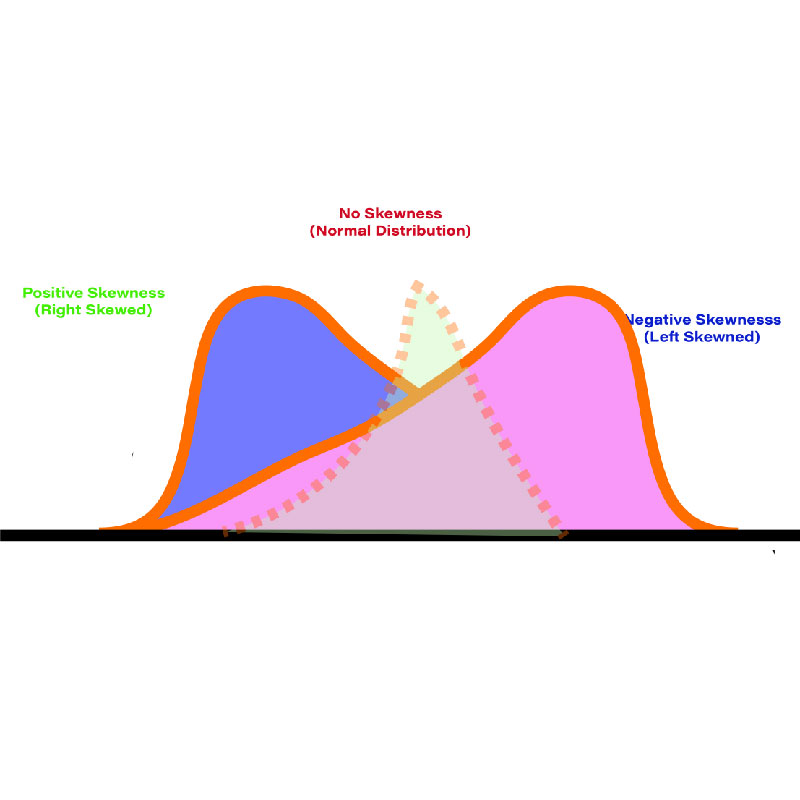
MEASURES OF SHAPE
When data is plotted onto a graph, the data is formed into the shape of a figure. This can help understand the characteristics of the data. Concepts discussed as Measures of Central Tendency and Variability are also applied. Our dataset is described in the form it is in, and by this, we're capable of describing the features of our data.
